As organizations increasingly move their applications, data, and infrastructure to the cloud, security testing has become more complex. Unlike traditional on-premise environments, cloud platforms operate under strict usage policies and a shared responsibility model. This makes cloud penetration testing not just a technical exercise, but also a compliance-driven activity.
Performing pentesting without understanding what cloud providers allow and restrict can result in service disruption, account suspension, or even legal action.
This blog explains what is permitted and what is not when conducting cloud pentesting on AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Cloud Pentesting and the Shared Responsibility Model
Cloud penetration testing focuses on identifying vulnerabilities in customer-managed assets by simulating real-world attack scenarios. Unlike on-prem environments, cloud providers retain control over the underlying infrastructure, while customers are responsible for securing what they deploy.
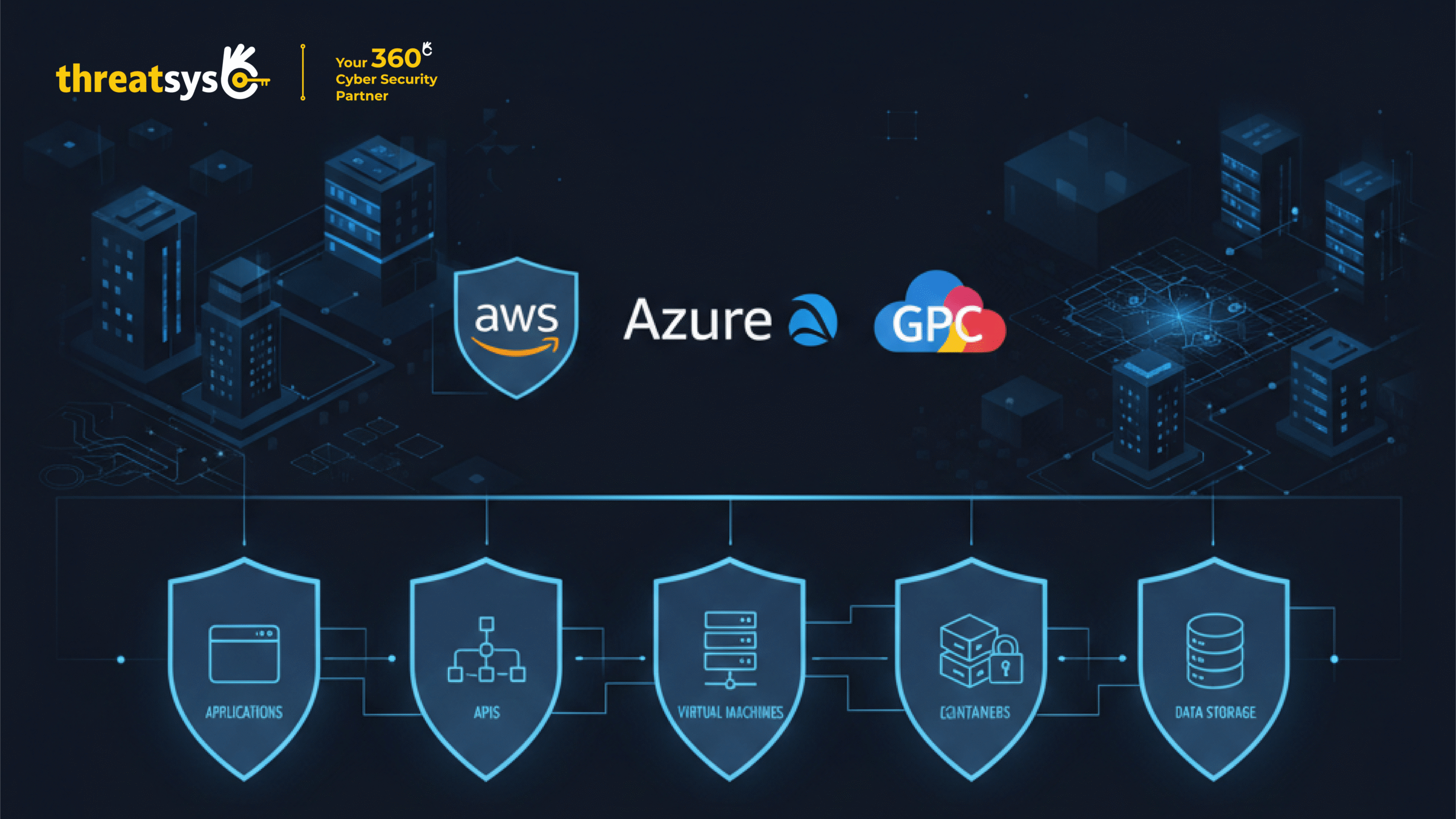
In general, customers are responsible for:
- Applications and APIs
- Virtual machines and containers
- Identity and access management (IAM)
- Network configurations and firewall rules
- Data storage and access permissions
Cloud providers, on the other hand, are responsible for the physical infrastructure, core networking, and managed services. Pentesting must always remain within the customer responsibility boundary.
AWS Cloud Pentesting Rules
Amazon Web Services allows penetration testing on customer-owned resources without prior approval, as long as activities follow AWS policies.
What Is Allowed on AWS
Organizations can perform security testing on:
- EC2 instances, containers, and Kubernetes workloads they own
- Web applications and APIs hosted on AWS
- IAM roles, policies, and privilege escalation paths
- Cloud misconfigurations and exposed storage services
- Authentication and authorization mechanisms
These tests must be controlled, scoped, and limited to assets within the customer’s AWS account.
What Is Not Allowed on AWS
AWS strictly restricts activities that could impact availability or other tenants, including:
- Denial-of-service or traffic flooding attacks
- Stress testing and load testing without approval
- Attacks against AWS infrastructure or shared services
- Phishing or social engineering campaigns using AWS
- Testing resources not owned by the customer account
Any form of DDoS simulation requires explicit authorization from AWS.
Microsoft Azure Pentesting Guidelines
Microsoft Azure permits penetration testing on customer-owned subscriptions and tenants without prior notification, provided testing stays within approved boundaries.
What Is Allowed on Azure
Permitted testing includes:
- Web application and API penetration testing
- Virtual machine and container security assessments
- Azure Active Directory and IAM configuration testing
- Privilege escalation and access control testing
- Cloud misconfiguration and exposure assessments
Testing must remain non-disruptive and confined to the organization’s own tenant.
What Is Not Allowed on Azure
Azure does not allow:
- Denial-of-service or stress testing
- Attacks on Microsoft-managed platform services
- Testing assets outside the organization’s tenant
- Social engineering, phishing, or malware simulations
Azure actively monitors abnormal behavior and may suspend services if violations are detected.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Pentesting Rules
Google Cloud Platform allows penetration testing on customer-owned projects as long as it complies with acceptable use policies.
What Is Allowed on GCP
Organizations can test:
- Applications and APIs running on GCP
- Network configurations and exposed services
- IAM roles, permissions, and privilege escalation
- Kubernetes and container security (GKE)
- Cloud configuration weaknesses
Testing can be performed without prior notice if limited to owned projects.
What Is Not Allowed on GCP
Restricted activities include:
- Denial-of-service and packet flooding attacks
- Phishing or social engineering campaigns
- Cryptomining simulations
- Attacks on shared Google infrastructure
- Testing outside the customer’s own projects
Aggressive scanning can trigger automated abuse detection systems.
Common Restrictions Across All Cloud Providers
Regardless of the cloud platform, certain activities are universally prohibited:
- Denial-of-service or stress testing without approval
- Social engineering and phishing attacks
- Malware propagation or outbreak simulations
- Attacks targeting other tenants
- Infrastructure-level testing of cloud providers
Cloud pentesting must always focus on customer-controlled assets and avoid service disruption.
Why Cloud Pentesting Requires Expertise
Cloud environments are dynamic, highly monitored, and API-driven. Traditional pentesting techniques, if applied incorrectly, can violate cloud policies or trigger automated defenses. This makes policy awareness and cloud-specific expertise just as important as technical skills.
Without proper scoping and methodology, even legitimate security testing can be mistaken for malicious activity.
How Threatsys Helps With Cloud Penetesting
![]()
Threatsys provides cloud-native penetration testing services designed specifically for AWS, Azure, and GCP environments. Our approach combines deep technical testing with strict adherence to cloud provider policies.
We help organizations:
- Identify misconfigurations, insecure identities, and exposed services
- Detect application and API vulnerabilities in cloud environments
- Simulate real-world attack paths without violating provider rules
- Reduce the risk of account suspension or service disruption
Threatsys delivers actionable remediation guidance aligned with cloud security best practices, compliance requirements, and business priorities that ensuring long-term cloud resilience.
Conclusion
Cloud penetration testing is essential, but it must be conducted responsibly and within cloud provider guidelines. Understanding what is allowed and what is restricted across AWS, Azure, and GCP enables organizations to test effectively without unnecessary risk.
With a policy-aligned and cloud-aware approach, businesses can strengthen their cloud security posture. Partnering with experienced cloud security specialists like Threatsys ensures that pentesting delivers real value while maintaining compliance.

Stay secure, stay aware with Threatsys.