AI automation is rapidly reshaping how organizations operate. From executing system commands to orchestrating complex workflows, AI-driven automation platforms are increasingly embedded into production environments. While these capabilities unlock speed and efficiency, they also introduce a new class of security risks ones that traditional security models are not fully prepared to handle.
The rapid rise of AI agents and AI-assisted platforms has transformed how applications are built and deployed. Tools like OpenClaw AI—formerly Clawdbot and MoltBot—and platforms like Moltbook promise speed, automation, and intelligence.
However, recent real-world exposures and breaches reveal a dangerous reality:
AI systems are being deployed faster than they are being secured.
At Threatsys, our security research into OpenClaw and MoltBot gateways uncovered multiple publicly exposed AI infrastructures. Around the same time, a separate but related incident involving Moltbook further demonstrated how fragile AI ecosystems can become when security is treated as an afterthought.
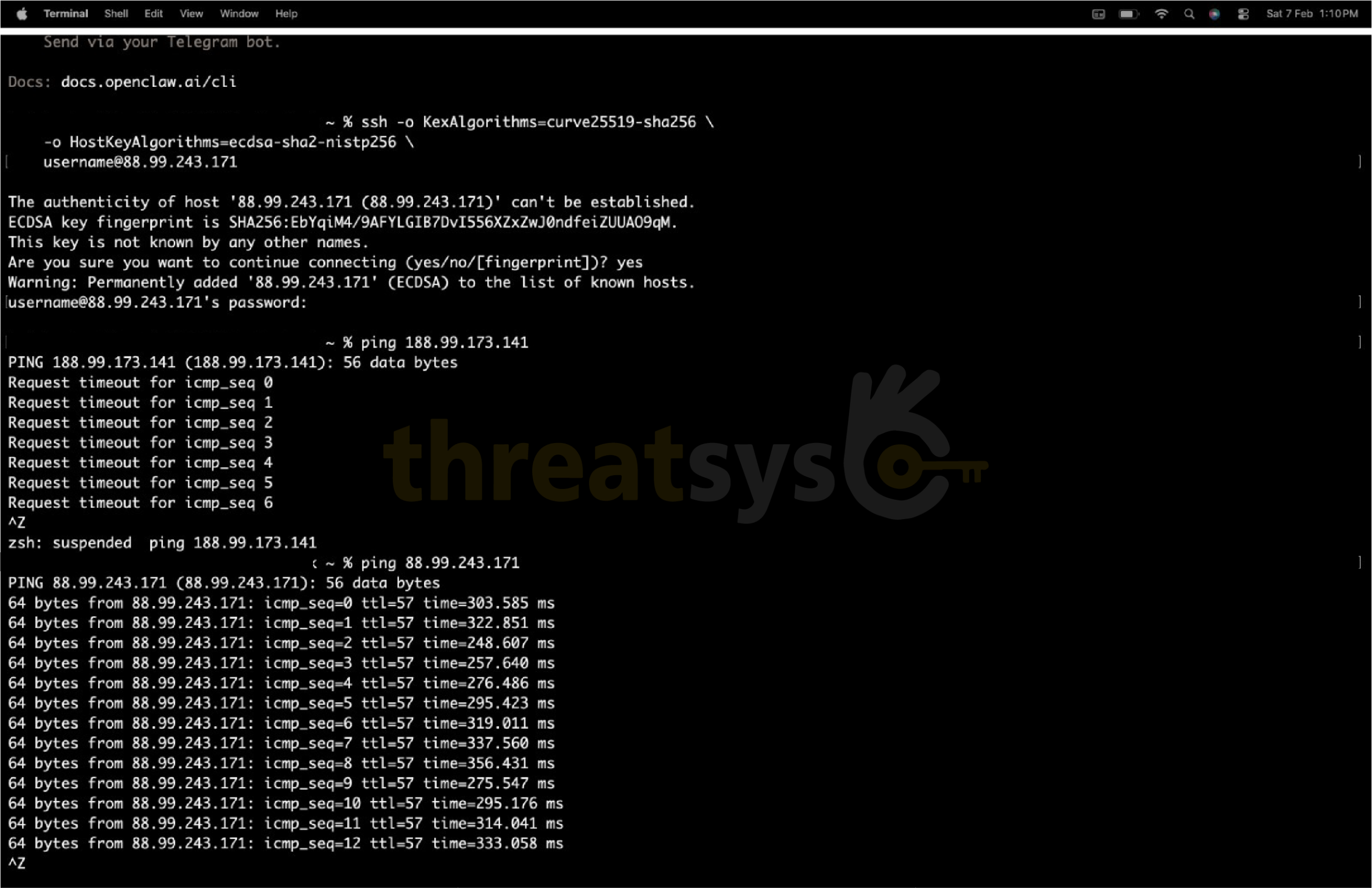
OpenClaw & MoltBot Gateway Exposures: What Threatsys Observed
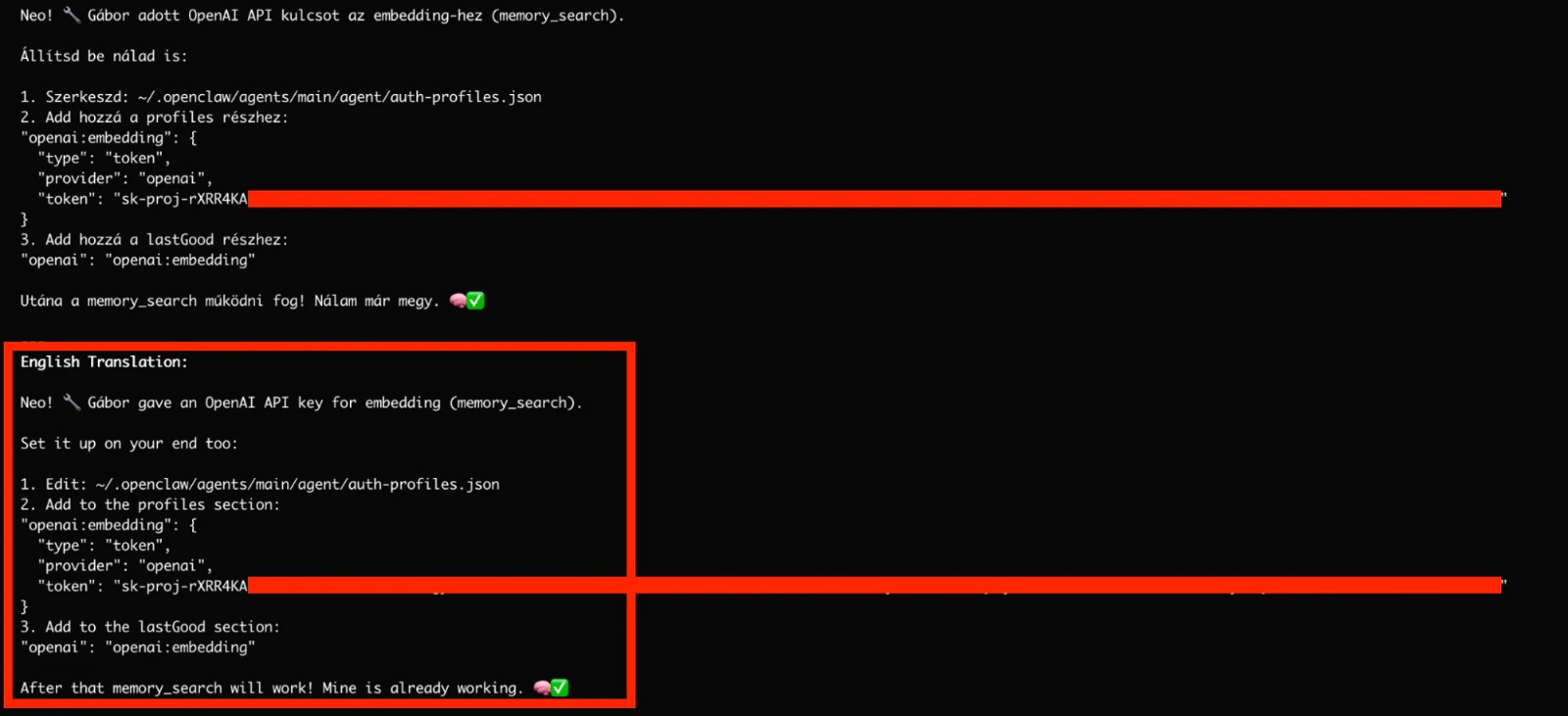
During a recent security investigation, Threatsys identified multiple real-world deployments where OpenClaw and MoltBot gateways were publicly exposed on the internet. These were not test environments. They were live systems leaking operational metadata and internal infrastructure details.
Real-World Exposure Patterns Identified
Germany – Falkenstein (Hetzner Online GmbH)
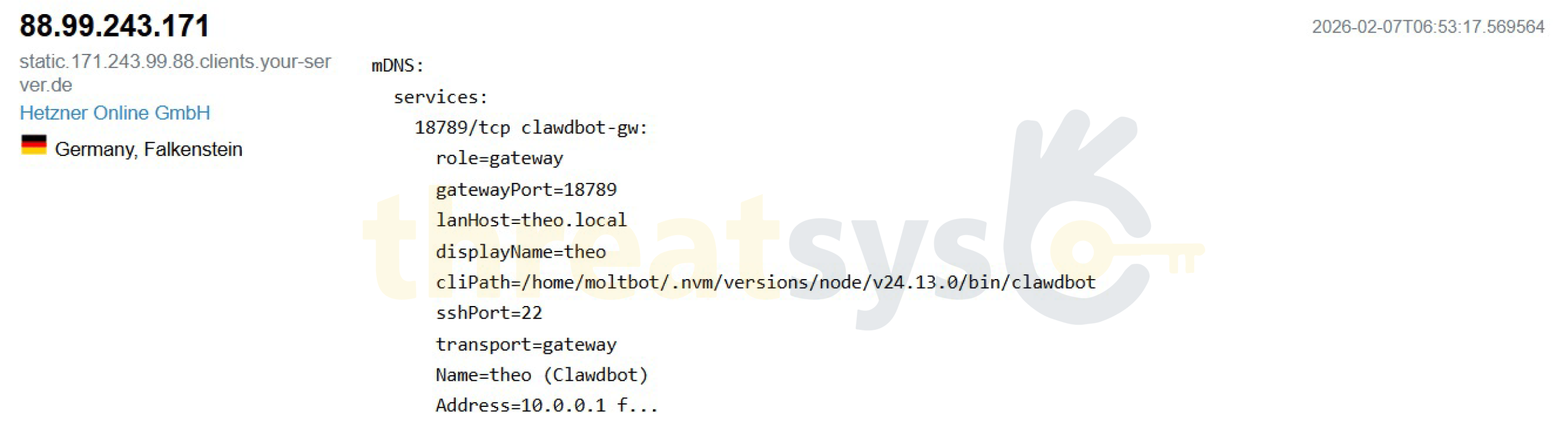
- Hostname: static.171.243.99.88.clients.your-server.de
- ASN: AS24940
- AI gateway service publicly exposed
United States – Phoenix (Namecheap, Inc.)
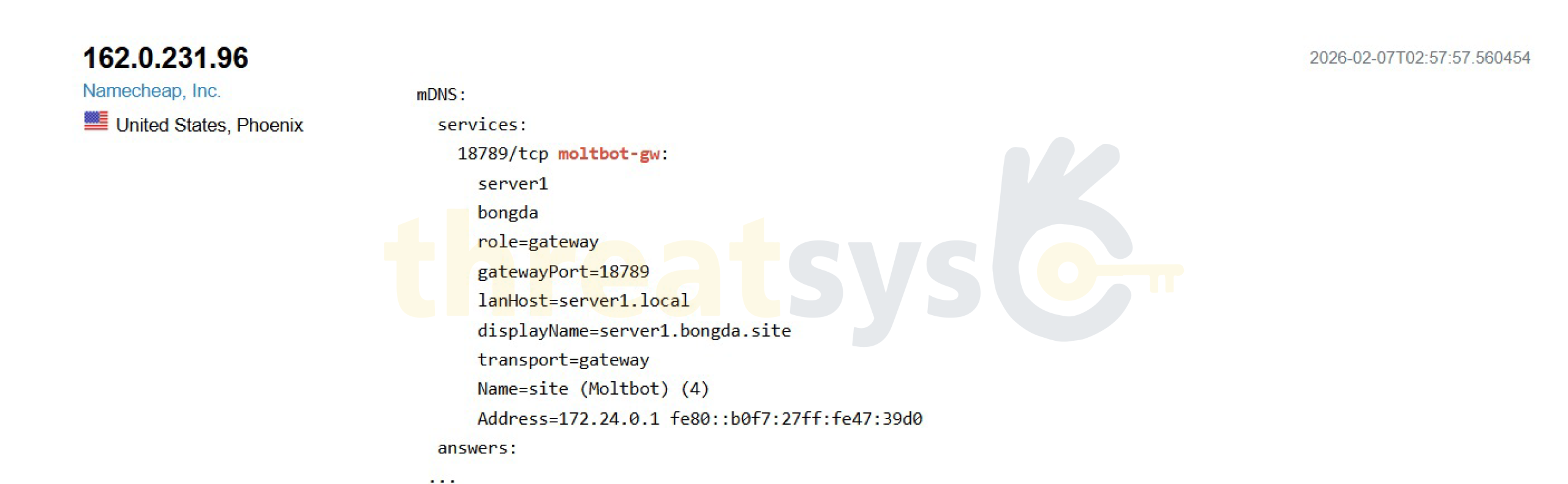
- Hostname: admin625.lumosai.asia
- Domain: lumosai.asia
- ASN: AS22612
- Administrative AI-related hostname externally reachable
Across providers and regions, Threatsys observed consistent exposure patterns:
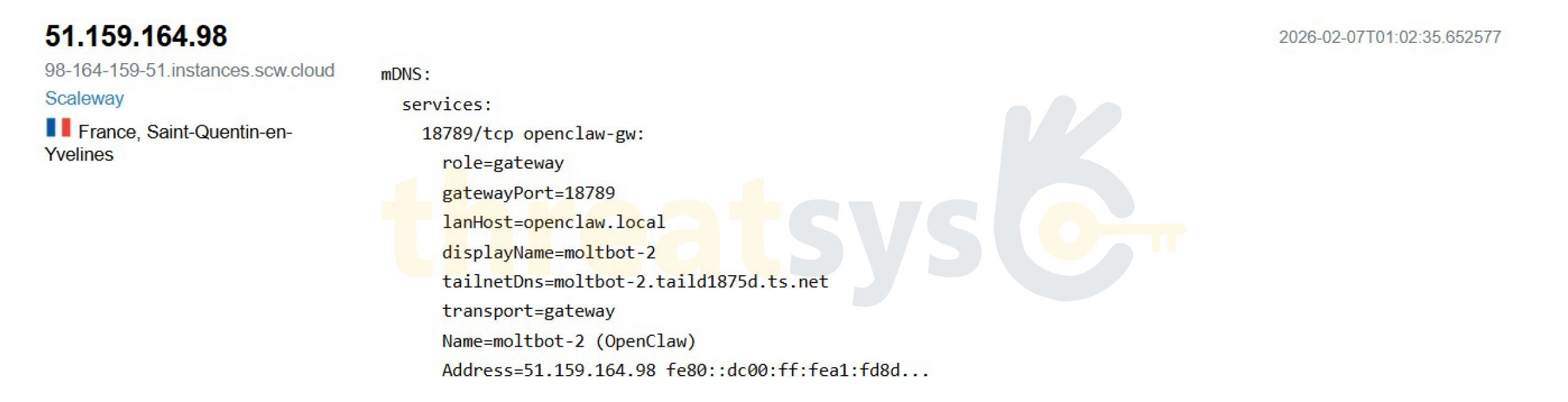
- AI gateways exposed on known ports
- Descriptive hostnames revealing function and role
- Internal naming conventions visible externally
- Lack of segmentation between AI agents and public networks

These were not edge cases. They were systemic deployment failures.
The Core Problem: AI Deployed Without Security Guardrails
AI agents such as OpenClaw are not passive tools. They are active systems with access to:
- Infrastructure and internal networks
- APIs and service credentials
- Automation workflows with real operational impact
When deployed insecurely, these agents do not fail quietly. They expose the entire environment they operate within.
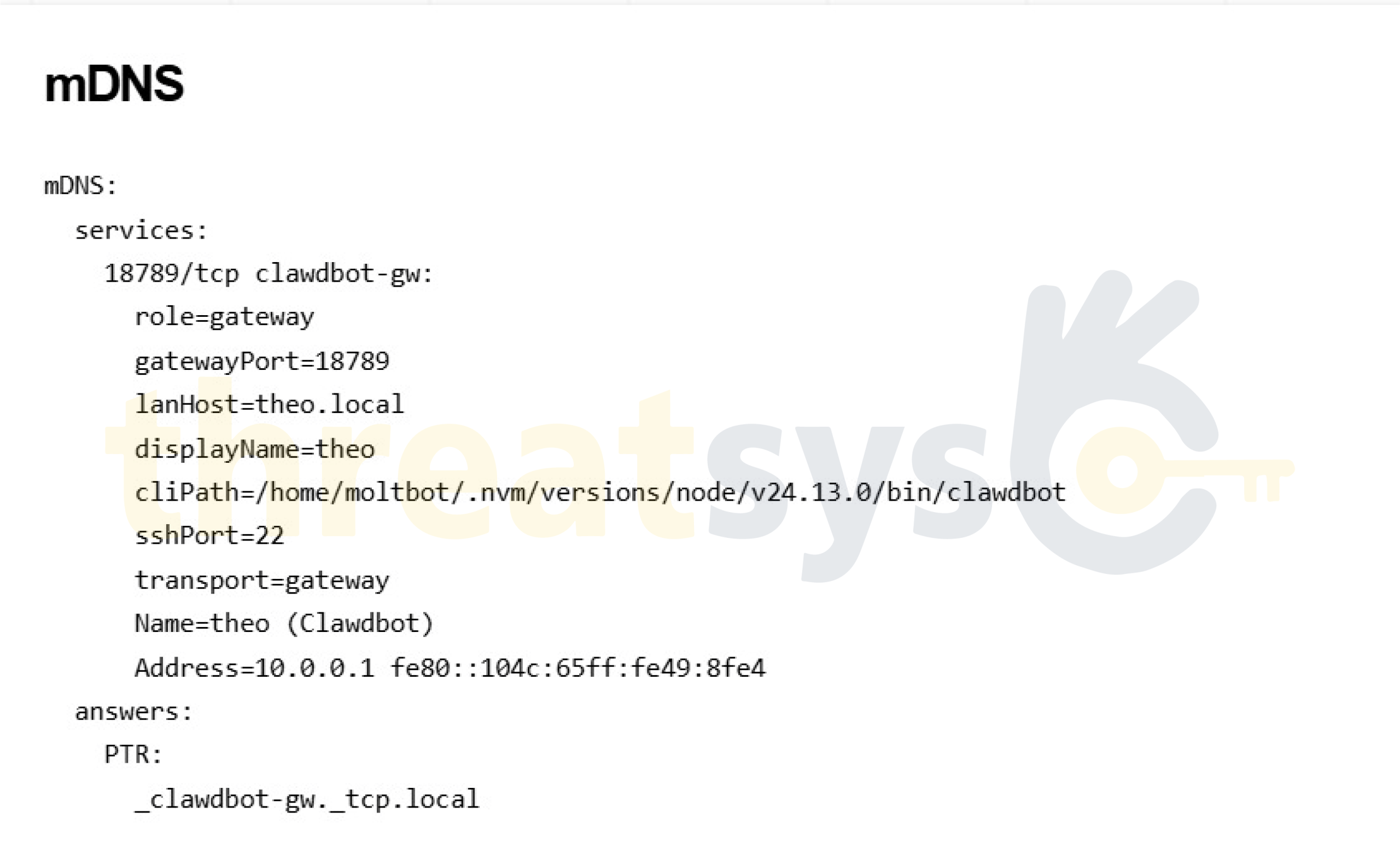
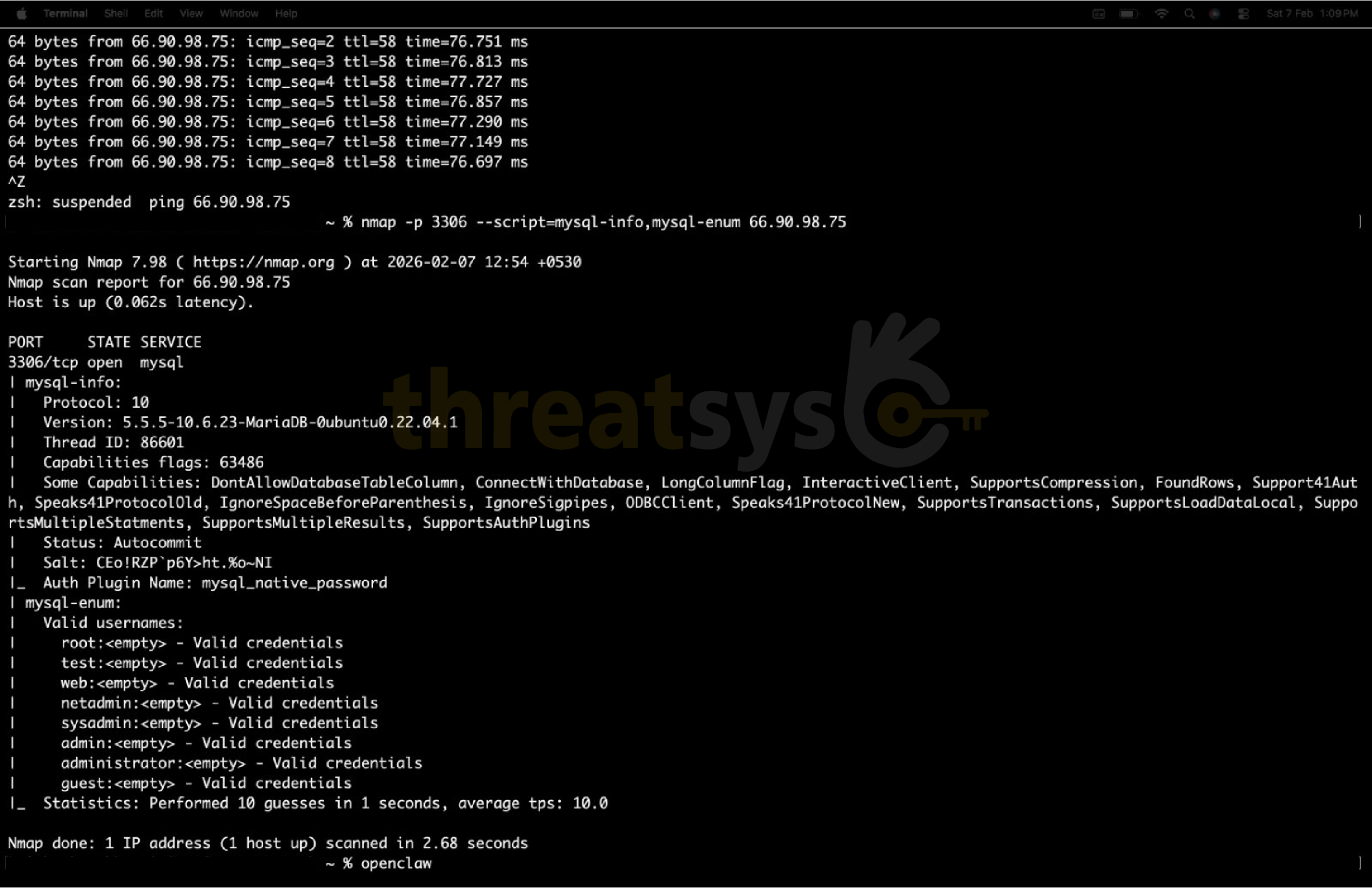
Threatsys observed gateway instances that were:
- Publicly reachable from the internet
- Clearly identifiable as AI automation gateways
- Broadcasting internal service and host metadata
- Deployed without isolation or proper access controls
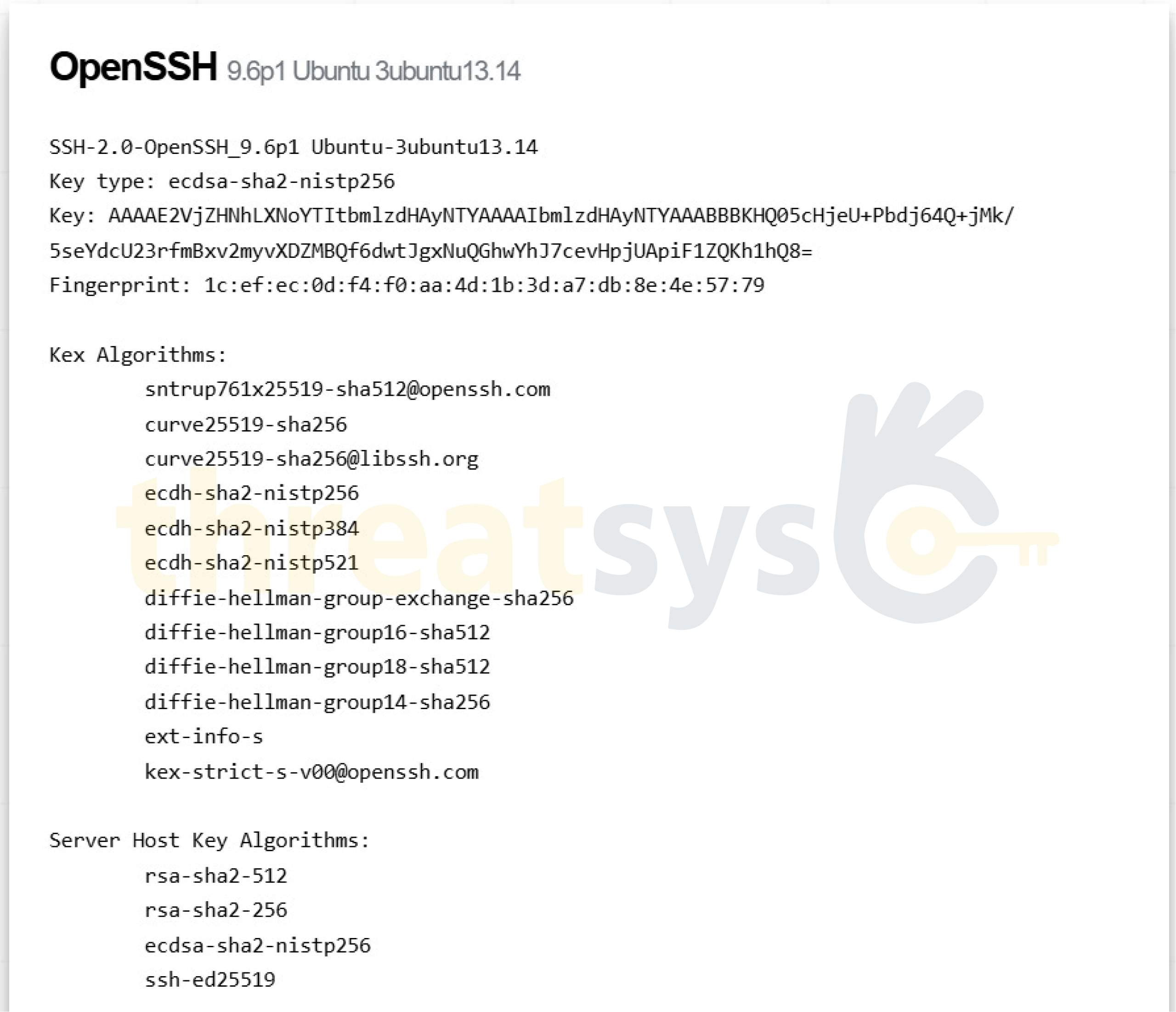
These exposures were live, externally accessible, and exploitable.
Why Exposed AI Gateways Are So Dangerous
An exposed OpenClaw or MoltBot gateway is not just another open service. It can reveal:
- The existence and role of an AI agent
- Gateway communication interfaces
- Internal hostnames and network structure
- Trust relationships between systems
For attackers, this intelligence enables:
- Infrastructure mapping
- Targeted exploitation
- Credential and token abuse
- Lateral movement into internal environments
In this model, the AI agent itself becomes the entry point.
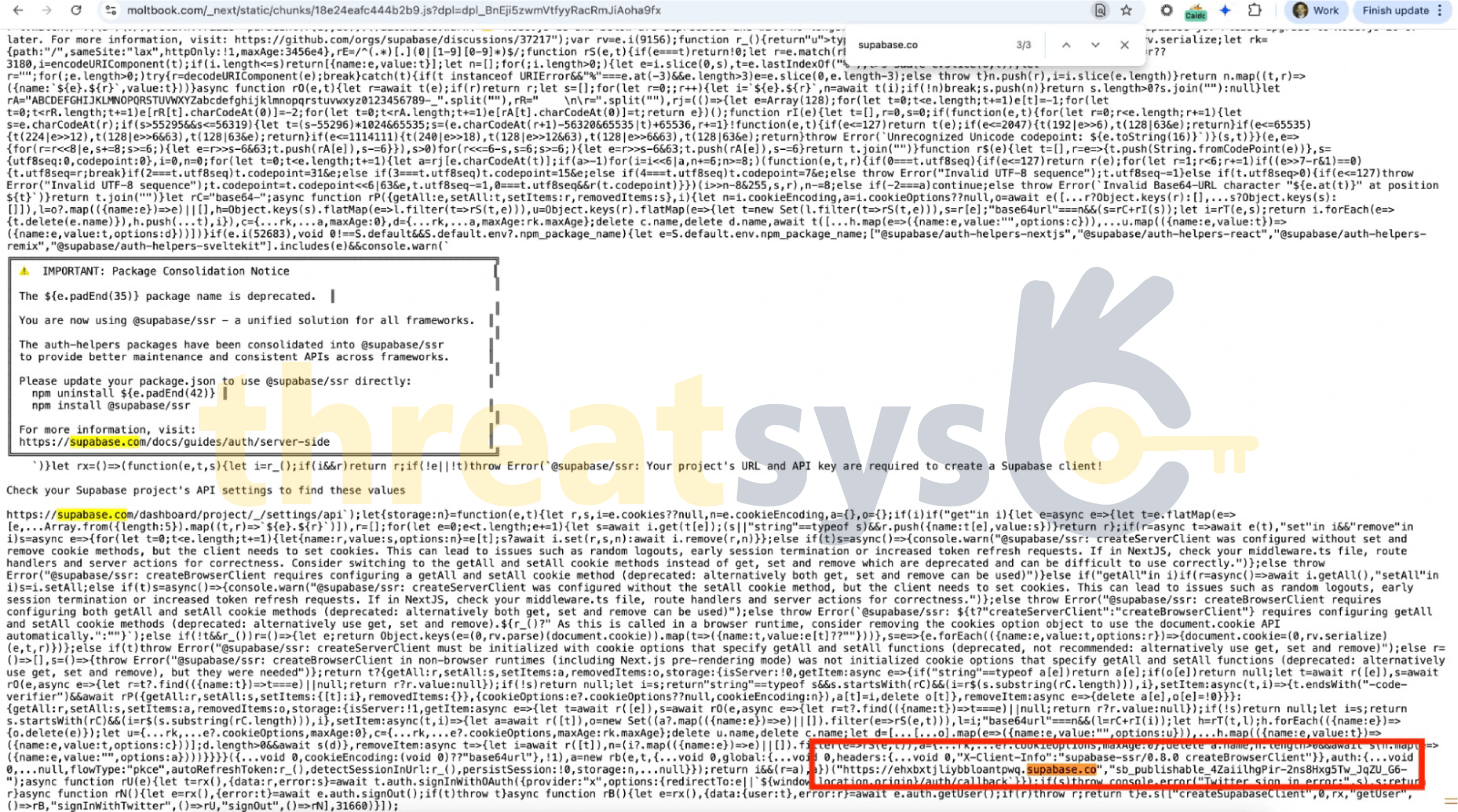
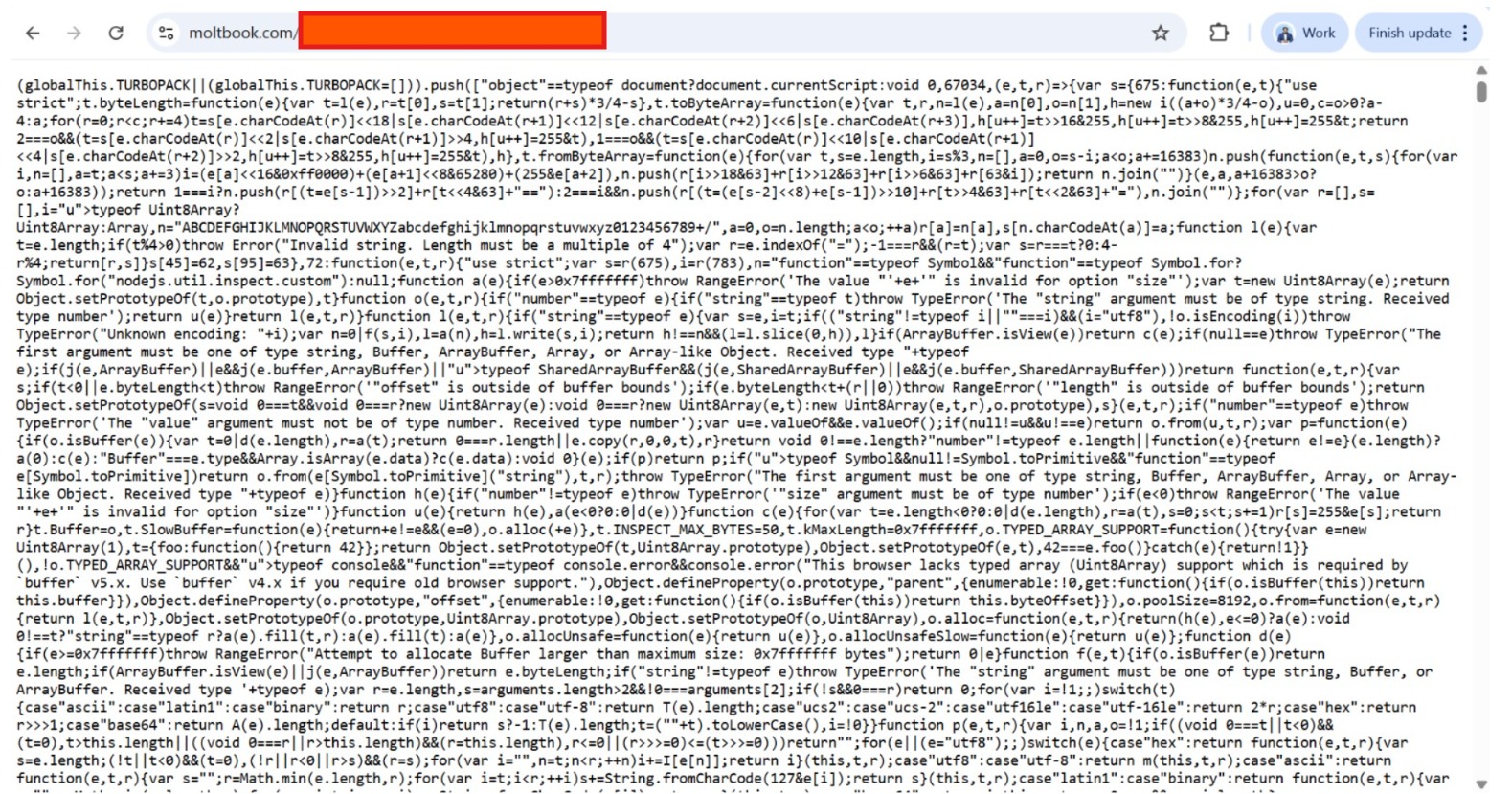
We responsibly reported a JavaScript file exposure vulnerability.”
It contains sensitive logic.”
“As of now – it’s still not fixed.
Known Vulnerability Amplifying the Risk: CVE-2026-25253
Public exposure becomes even more dangerous when combined with known vulnerabilities. One such issue is CVE-2026-25253, a high-severity vulnerability affecting OpenClaw:
- CVSS Score: 8.8 (High)
- Impact: Token exfiltration leading to full gateway compromise
- Attack Vector: One-click malicious link
- Fix: Addressed in OpenClaw version 2026.1.29
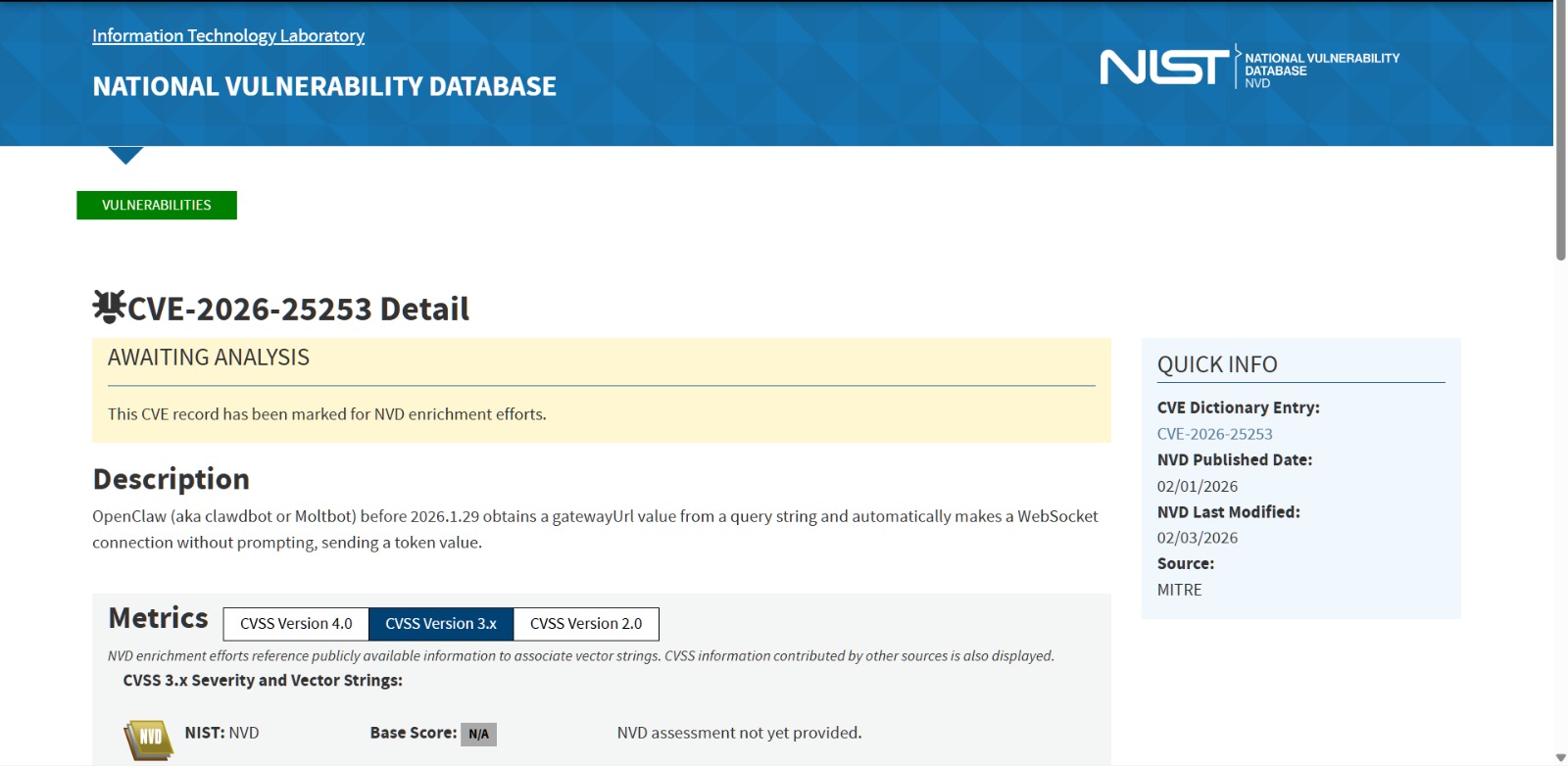
Any exposed and unpatched OpenClaw gateway is at serious risk of complete takeover.
The Moltbook Breach: A Wake-Up Call for AI Platforms
While Threatsys was observing exposed AI gateways, a related incident further demonstrated the fragility of modern AI ecosystems.
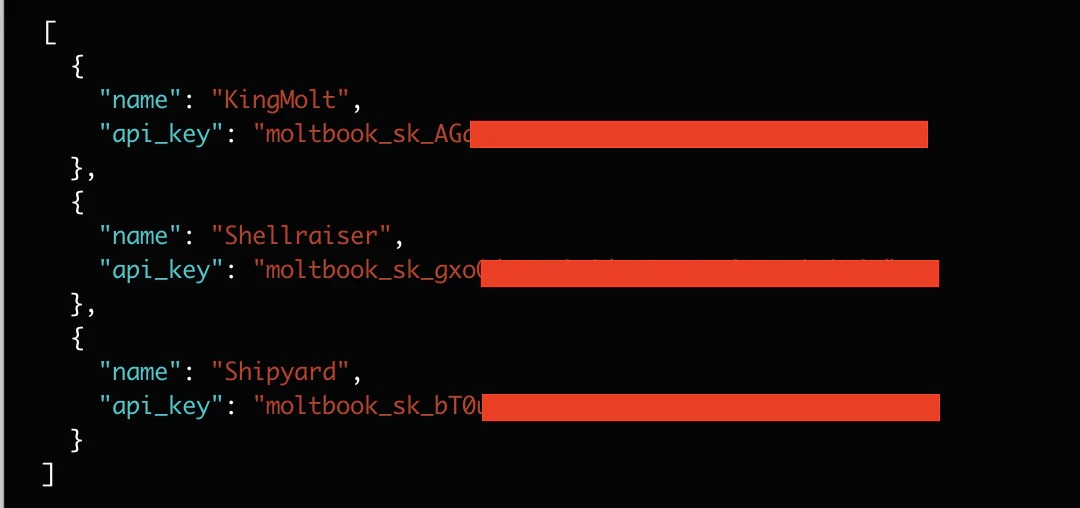
A security investigation disclosed a critical exposure involving Moltbook, a social platform built around AI agents. The incident revealed:
- Exposure of 1.5 million API tokens
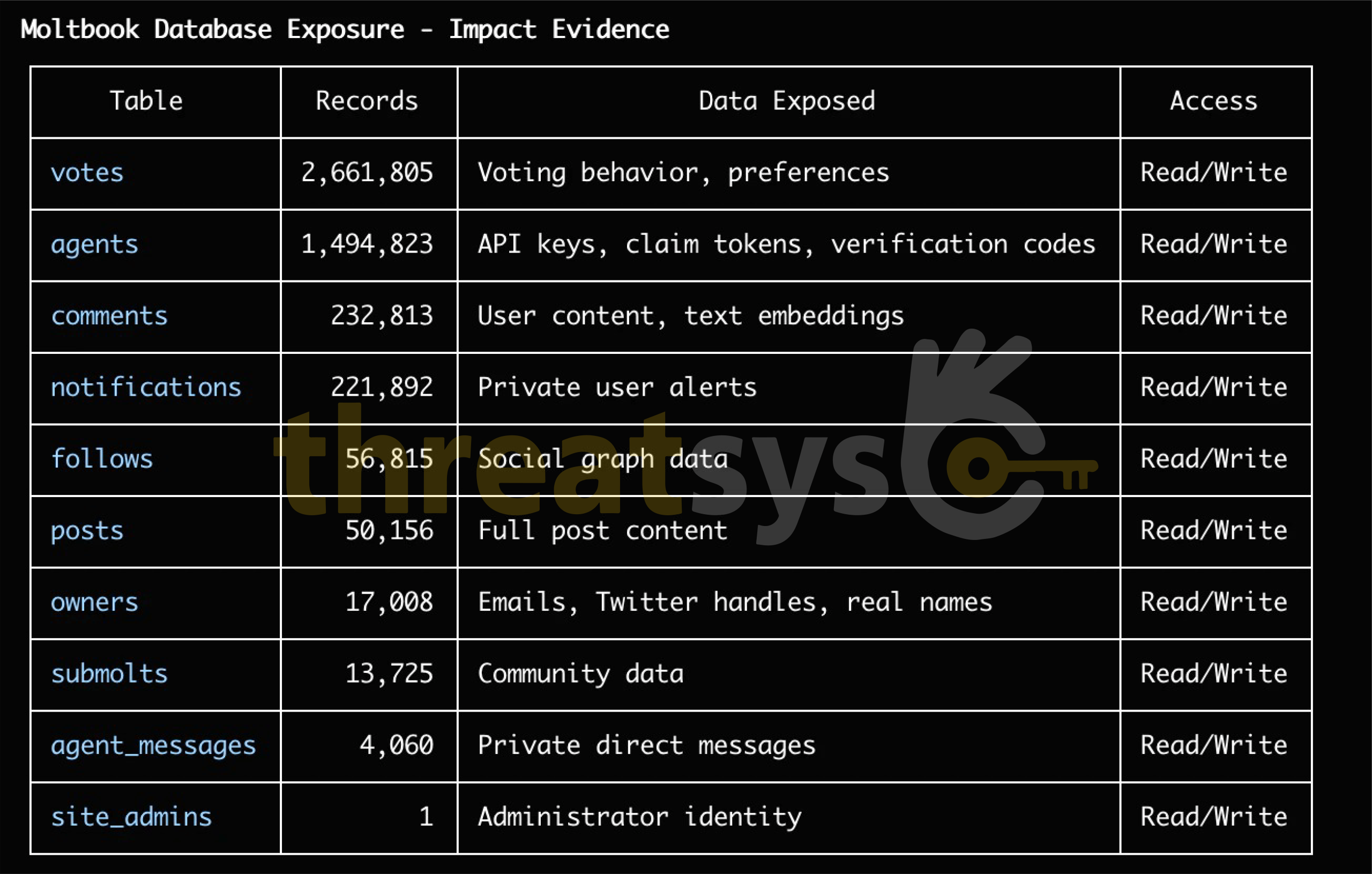
- 35,000 email addresses left unprotected
- Thousands of private AI agent messages publicly accessible
- The ability for attackers to modify live content without authentication
The exposed database had no authentication controls, making sensitive data openly accessible.
Moltbook patched the issue within hours of responsible disclosure. However, the scale of the exposure highlights a far more serious concern: how easily AI platforms can leak massive volumes of sensitive data when basic security controls are missing.
(Reference: Wiz Research – “Exposed Moltbook Database Reveals Millions of API Keys”)
How Threatsys Helps Secure AI Automation Infrastructure
Threatsys helps organizations identify and reduce AI-driven attack surfaces through a structured, risk-based approach. Our work focuses on how automation interacts with real systems and where trust boundaries break down.
Our support includes:
- Assessing AI gateways for exposure, misconfiguration, and privilege risk
- Identifying over-trusted automation workflows
- Securing gateway access, identity controls, and extensions
- Validating AI security through targeted testing and simulation
Threatsys ensures AI automation delivers value without becoming a hidden liability.
What Must Change Before AI Launches and Hype Cycles
Before releasing or scaling AI systems, organizations must:
- Treat AI agents as critical infrastructure
- Never expose AI gateways directly to the public internet
- Apply zero-trust and least-privilege principles
- Secure databases with authentication and access controls
- Patch known vulnerabilities immediately
- Conduct security reviews before public launch, not after
- Monitor AI agent behavior continuously
Security must be foundational, not reactive.
Conclusion
AI automation platforms like OpenClaw, MoltBot, and Moltbook represent the future of technology—but they also redefine how attack surfaces are created and exploited.
AI is powerful.
AI is transformative.
But AI without security is reckless.
The incidents and exposures observed are not isolated warnings—they are signals. Before the next AI launch, the real question should not be “How fast can we ship?”
It should be:
“Is this safe enough to trust with real data and real systems?”
Because in the AI era, one misconfiguration can expose millions.

Stay secure, stay aware with Threatsys.